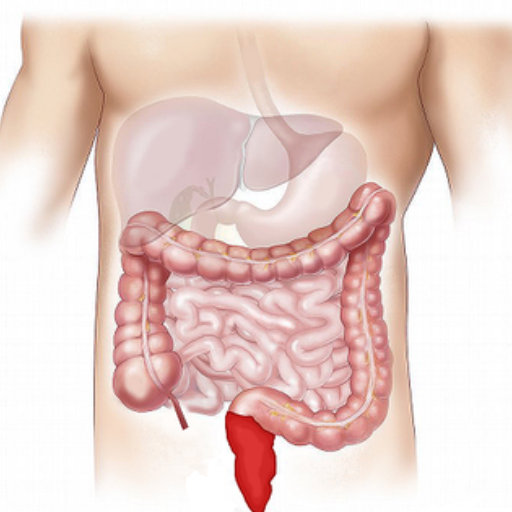
Colitis
Colitis refers to inflammation of the inner lining of the colon (large intestine), which can result in abdominal pain, cramping, diarrhea, and sometimes bleeding. There are various types of colitis, including ulcerative colitis, Crohn’s disease, ischemic colitis, infectious colitis, and microscopic colitis, each with distinct causes and characteristics. Ulcerative colitis and Crohn’s disease are chronic inflammatory bowel diseases (IBD) that can significantly impact a person’s quality of life.
These conditions may arise due to autoimmune reactions, infections, reduced blood supply to the colon, or other factors. Symptoms can range from mild to severe and may include urgent bowel movements, weight loss, fatigue, and in some cases, fever. Treatment depends on the underlying cause and severity but often includes medications to reduce inflammation and manage symptoms, dietary modifications, and in severe cases, surgery. Managing colitis involves regular monitoring and treatment adjustments to prevent flare-ups and complications, aiming to maintain a better quality of life for those affected.